ICS Industrial Control Systems was established in 2004. The company’s core business is the design,manufacture and implementation of machine vision systems, machines and inspection systems basedon Deep Learning technology, measuringmachines and marking machines. ICS also has experience inthe design and implementation of FLOW CONTROL SYSTEMS and TRACEABILITY production controlsystems.
In particular, ICS designs and supplies:
We carry out projects in Poland and many other European Union countries.
High-tech industrial applications are the challenge we take on in each of our projects. We build ourcooperation with customers based on professional competence and mutual trust.
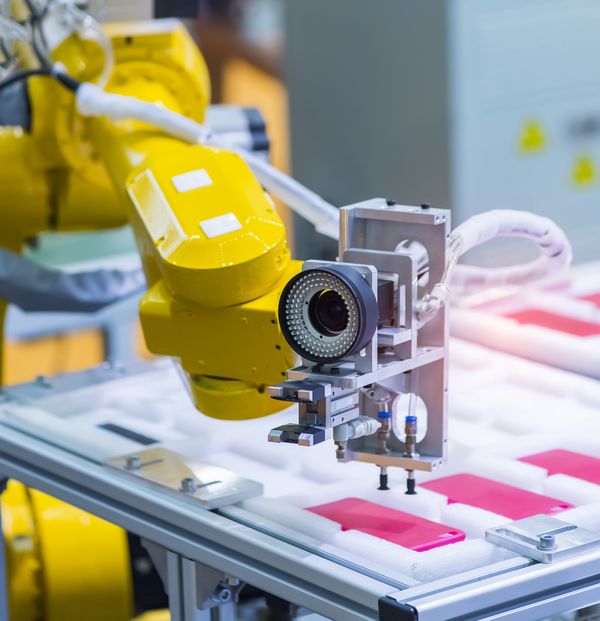

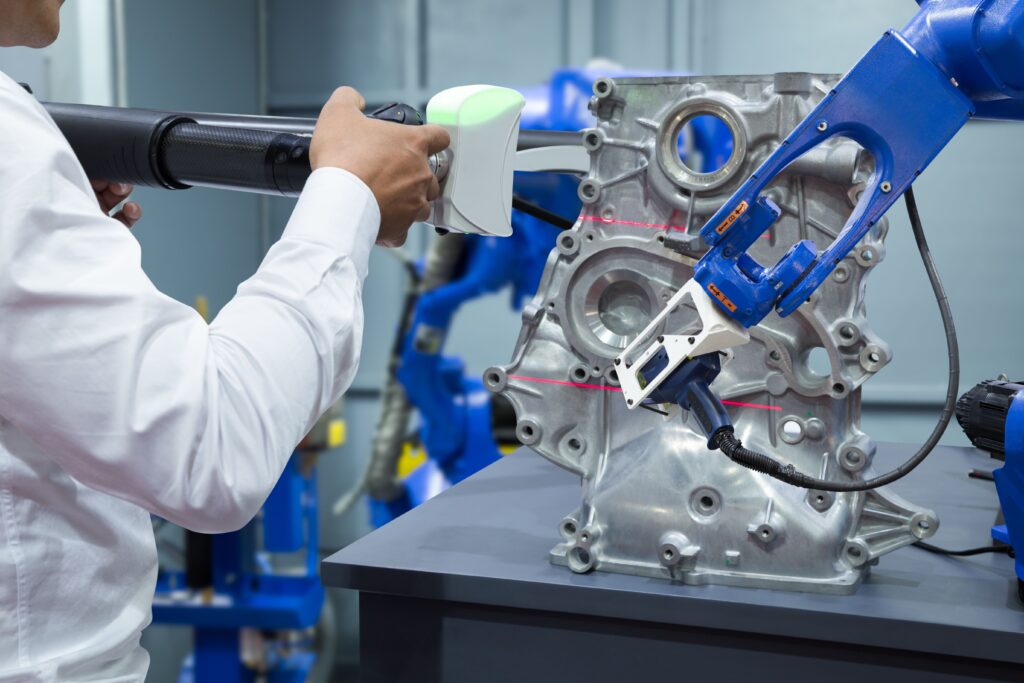
ICS has extensive experience in the design and implementation of machine vision systems. Machine vision systems are a field of technology that encompasses all 2D and 3D imaging, image processing, and analysis technologies to perform the following operations:
– Checking the presence or absence of a specific element or group of elements.
– Performing quality inspections, e.g., for assembly integrity or surface defects.
– Guidance/positioning, e.g., of a robot arm.
– Recognition/verification of alphanumeric characters (OCR/OCV).
– Reading codes, e.g., 1D barcodes and 2D Data Matrix.
– Performing precise optical measurements.
ICS has many years of experience in the design and implementation of machine vision systems.Machine vision systems are a field of technology that includes all 2D and 3D imaging, image processingand analysis technologies to perform the following operations:
A common approach to vision system applications is to provide a turnkey solution, i.e. completesystems that can be quickly and easily configured and integrated into a production line or machine.Vision systems are typically built from components such as optics (lenses), illuminators, cameras andsoftware. When designing and building a vision system, it is important to find the right balancebetween systemperformance and cost to achieve the best and desired result.
Deep Learning is a machine learning technique applied to vision systems that learns from trainingimages provided by the user and generates solutions for a wide range of image analysisapplications.Typical applications of Deep Learning in vision systems include:-detecting surface and shape defects.-identification of objects or images with respect to predefined classes.-localization, segmentation and classification of multiple objects within an image.-product quality analysis.-localization and classification of objects.-optical character recognition.
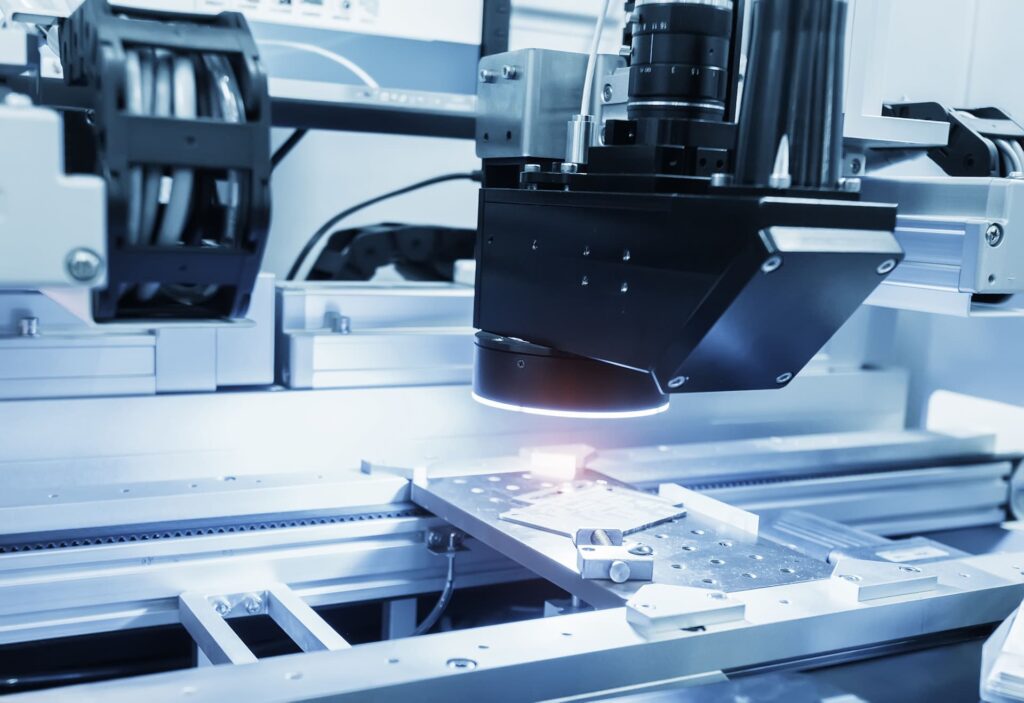

Cameras used in vision systems can be divided into two groups: area-scanning cameras (also calledarray cameras) and line-scanning cameras. The former is simpler and less technically demanding, whilethe latter is preferred in situations where array cameras are not suitable, for example, for scanninglarge areas, tapes that are in motion. Scanning cameras capture 2D images using a specific number ofactive elements (pixels), while line-scanning cameras are characterized by a single array of pixels.
Laser triangulation is a machine vision technique used to capture 3Dmeasurements by combininga laser light source with a camera. The laser beam and camera are aimed at the inspection target;however, by using a known angular offset (α) between the laser source and camera sensor, it is possibleto measure depth differencesusing trigonometry.

We are experienced in designing, programming and implementing quality control software.Our offerings include TRACEABILITY/FLOW CONTROL SYSTEMS type applications. Systems of this typeprovide communication between a database and production machines to archive production data andblock defective products so that they cannot be passed on to further production processes. Thiscommunication can be accomplished using company communicationnetworks, machine-specificcommunication protocols or using OPC (OLE for Process Control) technology.
The term “TRACEABILITY” means “traceability and origin.” It can also be translated as“traceability.” It refers to the completeness of information abouta product and each of its productionstages. A commonly accepted definition is that traceability is the ability to chronologically link uniquelyidentifiable units (parts, products) together in a verifiable manner. In other words, traceability is theability to verify the history of a product, its location through documented identification.
Currently, TRACEABILITY systems are generally dedicated systems. This is because it is difficultto develop and apply universal systems in such cases, which are characterized by very individualrequirements of data integration and functionality. Dedicated systems not only best solve the most important problems, but are also optimal in terms of implementation time and cost. Themanufacturing database created by these systems can be used by MES (Manufacturing ExecutionSystem) or ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems.
In particular, the TRACEABILITY system allows:
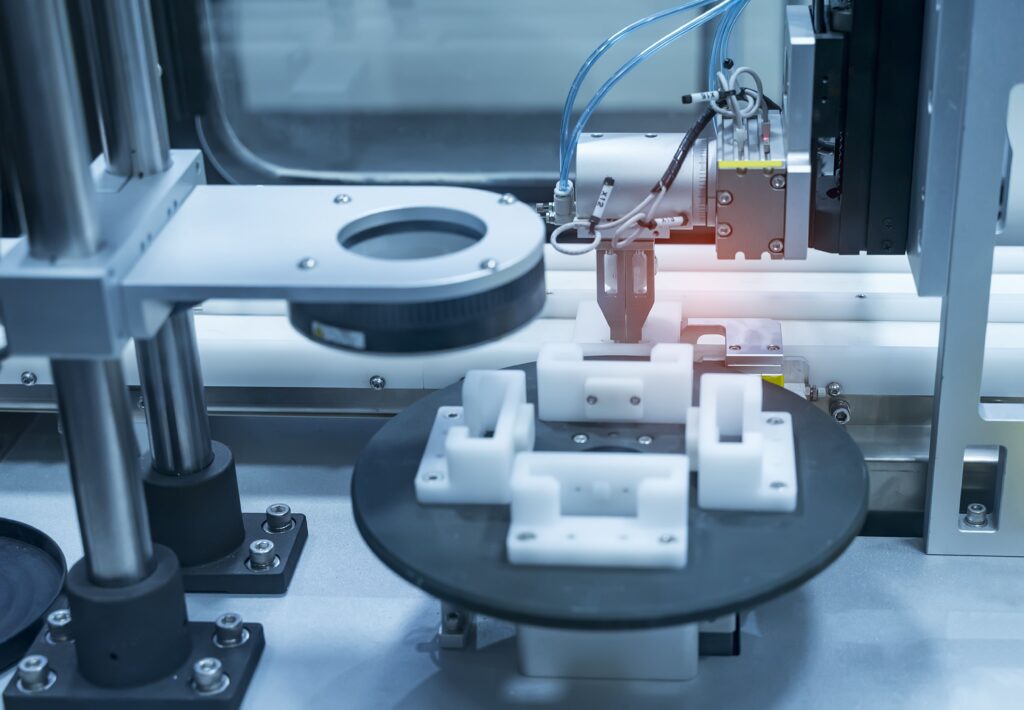

ICS has experience in the design and manufacture of quality inspection, measuring and markingmachines and equipment.
We use machine vision systems and precision measuring instruments for product quality inspection. We build machines based on precision telecentric optics and laser measurement technology.
Depending on application needs, we design machines and devices for:
We build machine control systems based on industrial computers and real-time operatingsystems and PLCs according to customer requirements.
We use both mechanical (impact) marking/engraving and laser marking/engraving in themachines we build.
ICS Industrial Control Systems
Mianowskiego 2B, 51-605 Wrocław
+48 609 625 129
email: k.skura@icsystems.pl
biuro@icsystems.pl
ICS Industrial Control Systems
ul. Wykładowa 53A, 51-520 Wrocław
NIP 898-111-36-98